Xcode was updated September 20th, 2019. Please see our new video here: more about Buildbox: http://www.buildbox. Launch Xcode 10 and go to your preferences menu. Then go to the 'Accounts' tab. Fill in your Apple iOS developer account details here. Once you're signed in, click 'Manage Certificate' and you'll get to this panel where you can see your existing certificates and provisioning profiles.
This guide shows how to set up your SDK development environment todeploy Cordova apps for iOS devices such as iPhone and iPad,and how to optionally use iOS-centered command-line tools in yourdevelopment workflow. You need to install the SDK tools regardless ofwhether you want to use these platform-centered shell toolsor cross-platform Cordova CLI for development. For a comparison of the twodevelopment paths, see the Overview.For details on the CLI, see Cordova CLI Reference.
Requirements and Support
Apple® tools required to build iOS applications only run on the OS Xoperating system on Intel-based Macs. Xcode® 8.0 (the minimum requiredversion) runs only on OS X version 10.11.5 (El Capitan) or greater, andincludes the iOS 10 SDK (Software Development Kit). To submit apps tothe Apple App Store℠ requires the latest versions of the Apple tools.
You can test many of the Cordova features using the iOS simulatorinstalled with the iOS SDK and Xcode, but you need an actual device tofully test all of the app's device features before submitting to theApp Store. The device must have at least iOS 9 installed, theminimum iOS version supported since the release of cordova-ios v4.4.0.
Installing the Requirements
Xcode
There are two ways to download Xcode:
from the App Store,available by searching for 'Xcode' in the App Store application.
from Apple Developer Downloads,which requires registration as an Apple Developer.
Once Xcode is installed, several command-line tools need to be enabledfor Cordova to run. From the command line, run:
Deployment Tools
The ios-deploy tools allow youto launch iOS apps on an iOS Device from the command-line.
To install it, run the following from command-line terminal:
Project Configuration
Installing Xcode will mostly set everything needed to get started with the native side of things.You should now be able to create and build a cordova project.For more details on installing and using the CLI, refer to Create your first app guide.
Deploying to Simulator
To preview the app in the iOS simulator:
Open the workspace file (
platforms/ios/HelloWorld.xcworkspace) from Xcode, or from the command line:Make sure the
HelloWorldVideo to audio converter freeware. project is selected in the left panel (1). Transfer data from pc to android over wifi.
Select the intended device from the toolbar's Scheme menu, suchas the iPhone XR Simulator as highlighted in (2)
Press the Run button (3) in the same toolbar to theleft of the Scheme. That builds, deploys, and runs theapplication in the simulator. A separate simulator application opensto display the app:
Only one simulator may run at a time, so if you want to test the app in a different simulator, you need to quit the simulator application and run a different target within Xcode.
Xcode comes bundled with simulators for the latest versions of iPhoneand iPad. Older versions may be available from the Xcode →Preferences.. → Components panel.
Deploying to Device
For details about various requirements to deploy to a device, referto the Launch Your App On Devices section ofApple'sAbout App Distribution Workflows.Briefly, you need to do the following before deploying:
Create a Provisioning Profile within theiOS Provisioning Portal.You can use its Development Provisioning Assistant to create andinstall the profile and certificate Xcode requires.
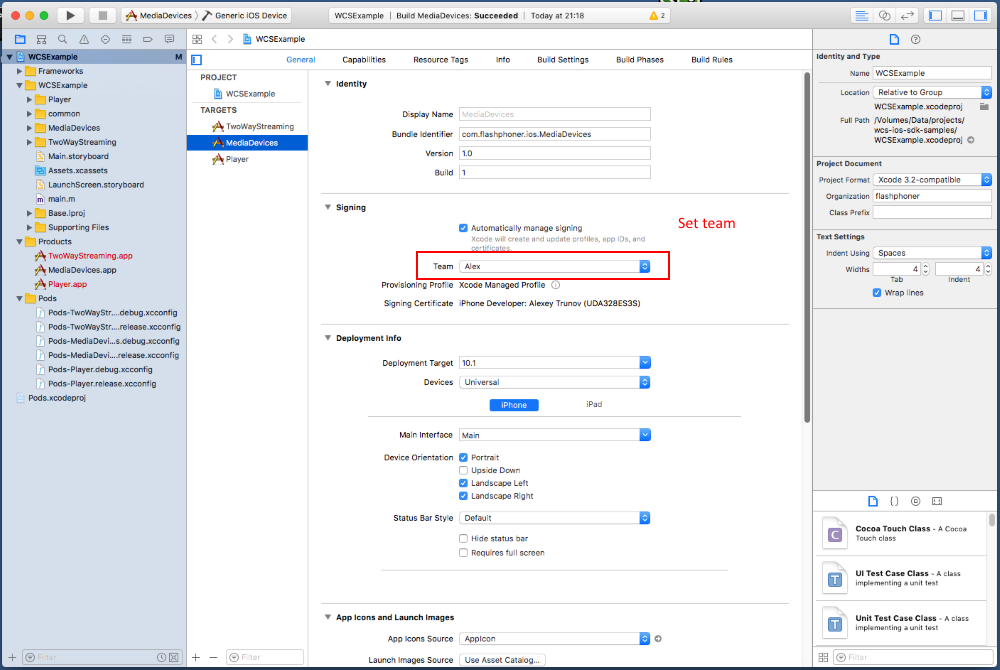
Verify that the Code Signing Identity setting within the Code Signing sectionwithin the build settings is set to your provisioning profilename.
To deploy to the device:
Use the USB cable to plug the device into your Mac.
Select the name of the project in the Xcode window's Schemedrop-down list.
Select your device from the Device drop-down list. If it isplugged in via USB but still does not appear, press theOrganizer button to resolve any errors.
Press the Run button to build, deploy and run the applicationon your device.
Signing an App
First, you should read through the Code Signing Support Pageand the App Distribution Workflows.
Using Flags
To sign an app, you need the following parameters:
| Parameter | Flag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Code Sign Identity | --codeSignIdentity | Code signing identity to use for signing. It can be created with Xcode and added to your keychain. Starting with Xcode 8 you should use --codeSignIdentity='iPhone Developer' both for debug and release. |
| Development Team | --developmentTeam | The development team (Team ID) to use for code signing. You would use this setting and a simplified Code Sign Identity (i.e. just 'iPhone Developer') to sign your apps, you do not need to provide a Provisioning Profile. |
| Packaging Type | --packageType | This will determine what type of build is generated by Xcode. Valid options are development (the default), enterprise, ad-hoc, and app-store. |
| Provisioning Profile | --provisioningProfile | (Optional) GUID of the provisioning profile to be used for manual signing. It is copied here on your Mac: ~/Library/MobileDevice/Provisioning Profiles/. Opening it in a text editor, you can find the GUID which needs to be specified here if using manual signing. |
| Code Sign Resource Rules | --codesignResourceRules | (Optional) Used to control which files in a bundle should be sealed by a code signature. For more details, read The OS X Code Signing In Depth article |
| Automatic Provisioning | --automaticProvisioning | (Optional) Enable to allow Xcode to automatically manage provisioning profiles. Valid options are false (the default) and true. |
Using build.json
Alternatively, you could specify them in a build configuration file (build.json)using the --buildConfig argument to the same commands. Here's a sample of abuild configuration file:
For automatic signing, where provisioning profiles are managed automatically by Xcode (recommended):
For manual signing, specifying the provisioning profiles by UUID:
Xcode Build Flags
If you have a custom situation where you need to pass additional build flags to Xcode you would use one or more --buildFlag options to pass these flags to xcodebuild. If you use an xcodebuild built-in flag, it will show a warning.
You can also specify a buildFlag option in build.json above (the value for the buildFlag key is a string or an array of strings).
Debugging
For details on the debugging tools that come with Xcode, see this articleand this video.
Open a Project within Xcode
Cordova for iOS projects can be opened in Xcode. This can be useful ifyou wish to use Xcode built in debugging/profiling tools or if you aredeveloping iOS plugins. Please note that when opening your project in Xcode,it is recommended that you do NOT edit your code in the IDE. This will edit the codein the platforms folder of your project (not www), and changes are liable to be overwritten.Instead, edit the www folder and copy over your changes by running cordova build.
Plugin developers wishing to edit their native code in the IDE should use the --link flag when adding theirplugin to the project via cordova plugin add. This will link the files so that changes to the plugin files in theplatforms folder are reflected in your plugin's source folder (and vice versa).
Once the ios platform is added to your project and built using cordova build, you can open it fromwithin Xcode. Double-click to open the ${PROJECT_NAME}/platforms/ios/${PROJECT_NAME}.xcworkspacefile or open Xcode from your terminal:
The screen should look like this:
Platform Centered Workflow
cordova-ios includes a number of scripts that allow the platform to be usedwithout the full Cordova CLI. This development path may offer you a greaterrange of development options in certain situations than the cross-platform cordova CLI.For example, you need to use shell tools when deploying a customCordova WebView alongside native components. Before using thisdevelopment path, you must still configure the SDK environmentas described in Requirements and Supportabove.
For each of the scripts discussed below, refer to Cordova CLI Reference for more information on theirarguments and usage. Each script has a name that matches the corresponding CLIcommand. For example, cordova-ios/bin/create is equivalent tocordova create.
External storage for laptop. To get started, either download the cordova-ios package fromnpm orGithub.
To create a project using this package, run the create script in the binfolder:
To run the app, use the run script in the bin folder:
The created project will have a folder named cordova inside that containsscripts for the project-specific Cordova commands (e.g. run, build, etc.).
To install plugins in this project, use the Cordova Plugman Utility.
Upgrading
Refer to this article for instructions to upgrade your cordova-ios version.
(Mac®, OS X®, Apple®, Xcode®, App Store℠, iPad®, iPhone®, iPod® and Finder® are Trademarks of Apple Inc.)
Xcode is the IDE endorsed by Apple for iOS development. The latest stable version is 6.0.1. It comes with the official iOS SDK.
For notes about using Logos and Theos with Xcode, see Xcode Logos.
- 1Developing application without iOS Developer program membership (aka without Provisioning Profile)
- 1.3Method 3 - other SDKSettings.plist modification
- 1.4Method 3: Old instructions (obsolete)
Developing application without iOS Developer program membership (aka without Provisioning Profile)
To develop for the device, one should first obtain a provisioning profile by joining the iPhone Developer Program (which costs $99). However, some simple tricks can be used to make Xcode compile and debug on jailbroken devices without provisioning profiles.
Related advice: Code Signing.
Method 1 - Command line
Works with Xcode 6.1 and earlier.
From the command line, cd to the Xcode project folder and line run:
Method 2 - SDKSettings.plist modification
See Building and Running iOS Applications Without A Paid Developer License for a guide. However, that guide is incomplete. Make sure to set ENTITLEMENTS_REQUIRED to NO and AD_HOC_CODE_SIGNING_ALLOWED to YES in your SDKSettings.plist along with setting CODE_SIGNING_REQUIRED to NO in the guide.
Method 3 - other SDKSettings.plist modification
Has been tested with Xcode 5.1.1, iOS 7.1 SDK and iPhone 5 running iOS 7.1.
What you need:

Before you start, do this just once:
Copy /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneOS*.*.sdk/SDKSettings.plist to your desktop.
Change
to
Save the file, and copy it back into the folder above, replacing the old file (needs admin permissions).
If you install a major Xcode update, you might need to repeat this process.
If you just did this and had Xcode open, restart it.
The actual signing part:
1. In the top left corner of Xcode, select 'iOS Device' as target. Go to build settings, and under Code Signing, select 'Don't Code Sign' in every available field.
2. Build with CMD+B, grab the .app folder from ~/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData//Build/Products//Your.app and copy somewhere like ~/Documents.
Note: should probably be 'debug-iphoneos'
Also, if you only want to try the app out yourself, just use AppSync Unified. Or, you can:
a. put AppSync Unified as a requirement for your package or,
b. put the following scripts in a postinst.
(by JJGadgets)
3. Put ldid in the same folder or closeby, navigate to that folder in Terminal and run the following command:
Note: the executable usually has the same name as the app with no file extension, in this case 'Your'.
Also, there should be no output. If you are getting output, for example
then you're doing something wrong and the app won't work.
Tip: If you're getting 'Permission Denied', type
4. Use SSH, iFunBox or similar to copy the app to /Applications.
5. In an SSH session, type:
(the path to the executable)
Or, open iFile, look for the executable and set permissions to 775 (User: RWE; Group: RWE; World: RE)
6. In the SSH session, type:
This should make your app appear on the homescreen. If it doesn't, respring or reboot.
Method 3: Old instructions (obsolete)
Xcode Build To Iphone Backup
These steps are designed for the most recent version of Xcode and iOS SDK, but should also work for versions after Xcode 3.2/iPhone SDK 3.x. If for some reason you are stuck with Xcode 3.1.x, try [1].
Compiling
Performing these steps allows you to use Xcode to compile any applications and deploy it yourself.
- 1. Create a self-signed code-signing certificate with the name 'iPhone Developer' on the 'login' (default) keychain using Keychain Access[1].
- 2. Open /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Info.plist (4.2 or below: /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Info.plist). You may need root permission.
- 3. Replace all occurrences of XCiPhoneOSCodeSignContext by XCCodeSignContext. There are three of them (XCode Version 3.2.4+).
- 4. Save the file and restart Xcode.
orIssue the following commands in terminal:
If you upgrade the iOS SDK, you need to perform steps 2 – 4 again.
Replacing codesign with ldid
These steps are necessary for debugging, since the entitlement can no longer be inserted by performing steps 1 – 4. To actually debug your app, make sure you have add -gta to Other Code Signing Flags of your target.
- 5. Make sure you have ldid on your Mac[2]. Place a copy somewhere e.g. in /usr/local/bin.
- 6. Create the a Python script ldid3.py right next to the ldid program. Make it executable. Fill it with:
- 7. Open iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec. This file can be found in:
| Xcode version | Path |
|---|---|
| 4.5 - 4.6 | /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/Specifications/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| 4.3 | /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/PrivatePlugIns/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| 4.2 | /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/PrivatePlugIns/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| Before 4.2 | /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/Plug-ins/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
- 8. Change the entry in the file from calling codesign to ldid3.py. Specifically:
- Convert the file to a human editable format (esp. in Xcode 4.6 or above). You may skip this if the file is already in plain-text or XML format.
- Replace the entry (which should be near the beginning of the file)with
Apple Xcode
Before you start, do this just once:
Copy /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneOS*.*.sdk/SDKSettings.plist to your desktop.
Change
to
Save the file, and copy it back into the folder above, replacing the old file (needs admin permissions).
If you install a major Xcode update, you might need to repeat this process.
If you just did this and had Xcode open, restart it.
The actual signing part:
1. In the top left corner of Xcode, select 'iOS Device' as target. Go to build settings, and under Code Signing, select 'Don't Code Sign' in every available field.
2. Build with CMD+B, grab the .app folder from ~/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData//Build/Products//Your.app and copy somewhere like ~/Documents.
Note: should probably be 'debug-iphoneos'
Also, if you only want to try the app out yourself, just use AppSync Unified. Or, you can:
a. put AppSync Unified as a requirement for your package or,
b. put the following scripts in a postinst.
(by JJGadgets)
3. Put ldid in the same folder or closeby, navigate to that folder in Terminal and run the following command:
Note: the executable usually has the same name as the app with no file extension, in this case 'Your'.
Also, there should be no output. If you are getting output, for example
then you're doing something wrong and the app won't work.
Tip: If you're getting 'Permission Denied', type
4. Use SSH, iFunBox or similar to copy the app to /Applications.
5. In an SSH session, type:
(the path to the executable)
Or, open iFile, look for the executable and set permissions to 775 (User: RWE; Group: RWE; World: RE)
6. In the SSH session, type:
This should make your app appear on the homescreen. If it doesn't, respring or reboot.
Method 3: Old instructions (obsolete)
Xcode Build To Iphone Backup
These steps are designed for the most recent version of Xcode and iOS SDK, but should also work for versions after Xcode 3.2/iPhone SDK 3.x. If for some reason you are stuck with Xcode 3.1.x, try [1].
Compiling
Performing these steps allows you to use Xcode to compile any applications and deploy it yourself.
- 1. Create a self-signed code-signing certificate with the name 'iPhone Developer' on the 'login' (default) keychain using Keychain Access[1].
- 2. Open /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Info.plist (4.2 or below: /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Info.plist). You may need root permission.
- 3. Replace all occurrences of XCiPhoneOSCodeSignContext by XCCodeSignContext. There are three of them (XCode Version 3.2.4+).
- 4. Save the file and restart Xcode.
orIssue the following commands in terminal:
If you upgrade the iOS SDK, you need to perform steps 2 – 4 again.
Replacing codesign with ldid
These steps are necessary for debugging, since the entitlement can no longer be inserted by performing steps 1 – 4. To actually debug your app, make sure you have add -gta to Other Code Signing Flags of your target.
- 5. Make sure you have ldid on your Mac[2]. Place a copy somewhere e.g. in /usr/local/bin.
- 6. Create the a Python script ldid3.py right next to the ldid program. Make it executable. Fill it with:
- 7. Open iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec. This file can be found in:
| Xcode version | Path |
|---|---|
| 4.5 - 4.6 | /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/Specifications/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| 4.3 | /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/PrivatePlugIns/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| 4.2 | /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/PrivatePlugIns/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
| Before 4.2 | /Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/Plug-ins/iPhoneOS Build System Support.xcplugin/Contents/Resources/iPhoneCodeSign.xcspec |
- 8. Change the entry in the file from calling codesign to ldid3.py. Specifically:
- Convert the file to a human editable format (esp. in Xcode 4.6 or above). You may skip this if the file is already in plain-text or XML format.
- Replace the entry (which should be near the beginning of the file)with
Apple Xcode
or
- 9. Save the file and restart Xcode.
If you upgrade the iOS SDK, you need to perform steps 8 – 9 again.
Allowing apps with invalid signatures to be installed
These steps allow you to install an unsigned app to the device. This method only works for iOS 4.0 or above.
- 10. Create a file /var/mobile/tdmtanf on the device, to enable Apple's 'TDMTANF bypass' in installd (warning: doing so will also put you in a sandboxed GameCenter[3]).
If you upgrade the firmware, you need to do step 10 again.
Automatically installing apps on your device wirelessly when they are built in Xcode
This is a simple Bash script that installs your app on your jailbroken iOS device whenever you build for iOS Device in Xcode. To set it up, go to Build Phases in your project settings and choose Editor > Add Build Phase > Add Run Script Build Phase in the menu bar. Set your shell to /bin/sh and paste this script in.
Make sure that you are able to SSH in as root without a password - set up SSH keypairs if you haven't already! Also establish that ldid is installed and in your $PATH.
References
- ↑Procedures can be found in http://developer.apple.com/mac/library/documentation/Security/Conceptual/CodeSigningGuide/Procedures/Procedures.html
- ↑If not, you can install from Fink, compile it from git://git.saurik.com/ldid.git, download it from https://github.com/downloads/rpetrich/ldid/ldid.zip or install it via homebrew
- ↑https://discussions.apple.com/thread/2745420?start=0&tstart=0

